FLASH FURNACE
Classification:
Product Introduction
Product Details
Refractory Configuration
| Used parts | Commonly used materials |
| Reaction tower | Electrofused rebonded magnesium-chromium bricks, electrofused semi-rebonded magnesium-chromium bricks, magnesium-chromium castables, etc. |
| Precipitation tank roof | Electrofusion reintegrated magnesium-chromium bricks, magnesium-chromium castables, etc. |
| Furnace wall under reaction tower | Electrofusion reintegrated magnesium-chromium bricks, etc. |
| Furnace wall under rising flue | Electrofusion bonded magnesium-chromium bricks, etc. |
| Furnace bottom of settling tank | Electrofused rebonded magnesium-chromium bricks, directly bonded magnesium-chromium bricks, magnesium sand filler, etc. |
| Rising flue | Electrofused rebonded magnesium-chromium bricks, electrofused half rebonded magnesium-chromium bricks, magnesium-chromium castables, magnesium-chromium compacts, refractory fiber plates, etc. |
Damage mechanism
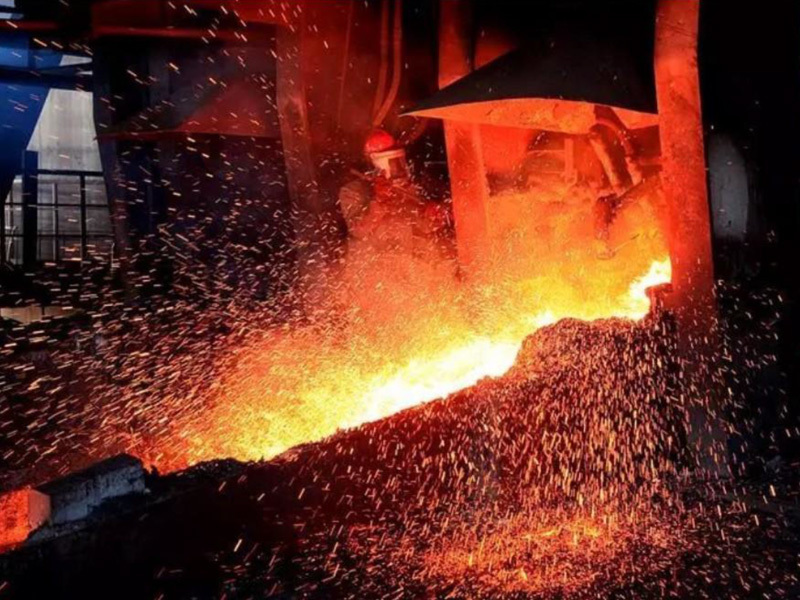
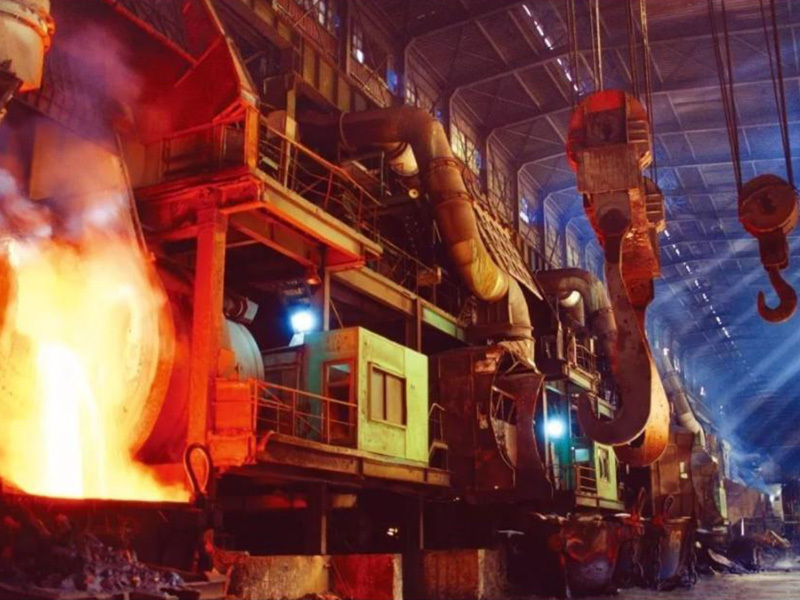
1, reaction tower in the lower part: high temperature melt and gas flow on the refractory lining will have erosion, mechanical scouring and thermal shock.
2, the top of the reaction tower: the temperature is relatively low, the degree of erosion is relatively light, the part of the material damage is mainly thermal spalling
3, sedimentation tank slag line area: the most vulnerable to viscous liquid slag scouring, while the metal copper, slag and refractory materials generated by the reaction of low eutectic gradually lost refractory melt damage.
4, the bottom of the furnace: the degree of erosion is relatively low, but due to the large amount of feed, the bottom lining needs to withstand greater pressure, and direct contact with the melt, easy to penetrate the erosion.
5, the upper part of the settling tank: mainly by the high temperature gas flow thermal radiation, erosion is relatively low.
6, rising flue: mainly by the hot gas flow radiation, the windward side of the soot scouring, the temperature is slightly lower.
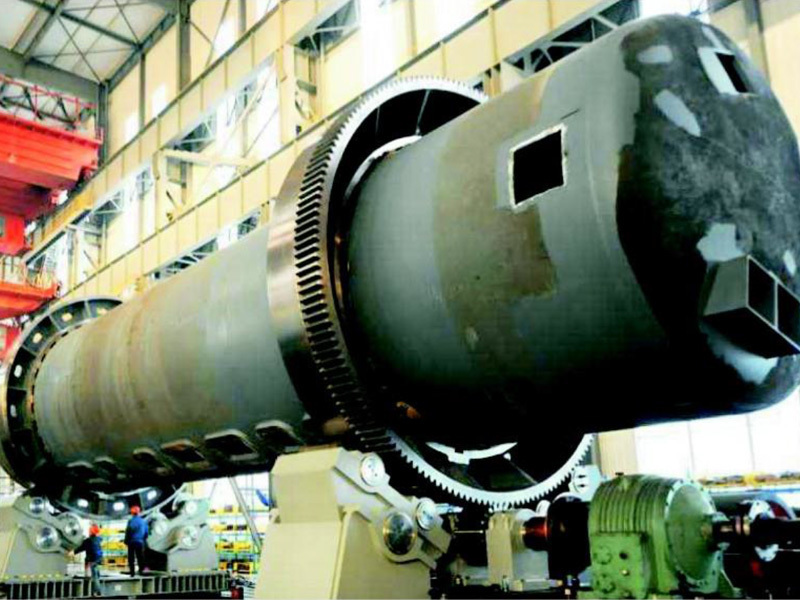
Product Show

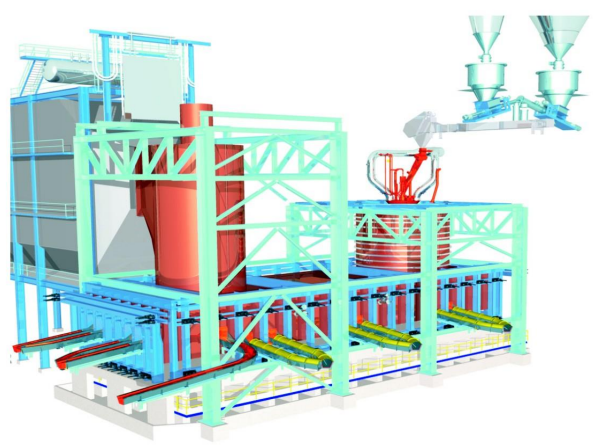
Key words:
FLASH FURNACE









